News Business
Business
CRSS and the Construction Industry
The two most important schemes available to employers and businesses across the country at this time are the CRSS (Covid Restrictions Support Scheme) and EWSS (Employment Wage Subsidy Scheme). Under the current CRSS guidelines, the construction industry is not permitted to make a claim under CRSS as they do not satisfy the guidelines whereby they operate from a fixed premises that is required to prohibit or considerably restrict customers from accessing their premises. They may still be eligible to claim the EWSS wage subsidy.
To learn more about this contact Brendan Murphy, Tax Partner at Roberts Nathan brendan.murphy@robertsnathan.com or call (01) 876 4550.
January 28, 2021
Company Acquisitions & Disposals
Deal Done – EnviroChemie Group acquires IWM
EnviroChemie Group, headquartered in Germany and a subsidiary of SKion Water GmbH, has acquired Dublin-based Industrial Water Management Ltd. (IWM) for an undisclosed sum.
Founded in 1976, EnviroChemie supplies sustainable system solutions worldwide for all the tasks involved in industrial water treatment and the treatment of process water, circulation water, cooling water, boiler water and wastewater.
IWM specializes in cooling tower, steam boiler and water hygiene services, including legionella control and water chemicals supply. With 30 employees, IWM generates an annual turnover of approximately €3m.
DWF Dublin (Ross Little, Head of Corporate) advised the shareholders and management of IWM on the legals, and Derek Dervan (Partner in Roberts Nathan) provided corporate finance and tax advice to the shareholders and management of IWM.
January 26, 2021
Brexit
Brexit deal done; What next?
Aidan Scollard, Partner at Roberts Nathan, provides his view on what Irish businesses dealing in cross-border trade with the UK need to consider following the recent Brexit agreement between the European Union and United Kingdom of the Free Trade and Cooperation Agreement.
The Deal
The (European Union) EU and the United Kingdom (UK) finally reached agreement on a Free Trade and Cooperation Agreement (TCA), avoiding a hard Brexit and the risks of duties and tariffs under WTO rules. However, this does not change the fact that the UK has left the EU and therefore is no longer part of the EU single market and customs union and is now regarded as a third country. This status has significant consequences for businesses in different areas such as cross border trade, the imposition of VAT on transactions and the free movement of people.
At 1,246 pages and affecting over $900 billion worth of goods and services, the TCA is the most ambitious and far-reaching trade agreement ever concluded by the EU. Irish businesses will need to fully comprehend the effect of the TCA on cross-border trade between the EU and UK.
A new Partnership Council, co-chaired by the European Commission and the UK government, will oversee the agreement’s implementation and management. A large number of committees and working groups will be established to oversee the details of new arrangements at a more-granular level, including resolving any technical issues arising from the agreement or ensuring proper functioning of new rules.
The new UK-EU relationship is fluid, and these bodies will be making judgments and issuing guidance that will have the potential to change market access and frameworks. In short, things are likely to change and there will be an extended period of adjustment.
Highlights
Further review of particular aspects of the TCA will be required in the coming months, but in the meantime we set out some highlights of the main initial impacts of the TCA:
TARIFF AND QUOTA FREE TRADE OF GOODS
- The TCA establishes zero tariffs or quotas on trade between the UK and the EU, where goods comply with rules of origin requirements.
- Notwithstanding the tariff and quota free trade enshrined in the TCA, certain technical barriers to trade continue to apply and address issues related to technical regulation, conformity assessment, standardisation, accreditation, market surveillance and marketing and labelling.
- While Brexit ends the EU ease and simplicity of moving goods freely, the TCA adds administrative burdens and no duty or tariff taxes.
- The TCA includes well-established provisions on cross-border trade in services that will secure continued market access across a broad range of sectors, including professional and business services, financial services and transport services, and will support new and continued foreign direct investment.
- In relation to financial services, although the TCA provides for “continued market access” the details have been left for later. The EU and the UK are yet to discuss “specific equivalence determinations” which will eventually be codified in a Memorandum of Understanding.
- The UK and the EU have agreed a framework for the recognition of professional qualifications which is based on the EU’s recent free trade agreements.
- The effect of Brexit and the TCA on cross-border trade in services differs from sector-to-sector. For example, UK resident financial services firms previously possessed “passporting rights” which allowed them to sell financial services into the EU. The TCA has not granted equivalent rights meaning that on 1 January 2021 UK resident financial firms will (as expected) lose their right to sell financial services in the EU.
- One of the key issues of concern of the EU was ensuring that the UK could not grant subsidies (tax or otherwise) to UK businesses which would effectively allow them to undercut similar businesses in the EU.
- The EU and UK are free to determine their own rules relating to the granting of subsidies but are bound by broad principles which must inform the contents of the rules which must ensure that the granting of a subsidy does not have detrimental effects on the trade between the EU and UK.
- The EU and UK shall each establish independent bodies which will design and oversee these rules and which are subject to the review of their respective domestic courts.
- The EU and UK have agreed on a reciprocal dispute resolution mechanism (an accelerated arbitration procedure) where a party is of the opinion that a subsidy is causing, or is at risk of causing, significant harm to its industries.
- Whilst part of the EU, the UK was bound by EU laws related to state aid and government subsidies and was subject to oversight by the European Court of Justice (EUCJ), a sore point for the UK public. Brexit effectively removes the applicability of these laws and jurisdiction of the EUCJ.
- There is also a ‘most-favoured nation’ clause, which ensures that, if either the UK or the EU gives more-favourable terms to another country in future, those terms will automatically extend to the UK/EU deal.
- However, these provisions are subject to a long list of exceptions, which vary from one member state to another.
- Residence rights in existing cases in the UK and EU will continue to be respected as long as the residence situation remains unchanged. New residency applications after the transition period will likely be subject to the same procedures as for third countries.
- Existing (frontier) workers will have the right not to be discriminated against on grounds of nationality as regards employment, remuneration and other conditions of work and employment. In addition, they will have the right to take up and pursue activities and assistance by employment offices in the same way as offered to own nationals as well as rights to tax, social advantages, housing benefits and access to education for their children.
- Prior to Brexit, UK citizens (like all other EU citizens) were granted unrestricted rights to live and work in the EU, and vice versa. Post Brexit, closer consideration will be required for non-EU workers and transfers, however the UK / Ireland Common Travel Area provisions allow for continuation of citizens of each of those countries to live, work and retire to each other’s jurisdiction.
January 8, 2021
Business in Ireland
RN Podcast: 2020 – The Year that was, and 2021 potential for business growth
As we close out on 2020, we have produced a podcast where we take a look at the year that was, and provide our view on what businesses might expect in 2021. Aidan Scollard, Brendan Kean and Derek Dervan, partners with Roberts Nathan discuss three main areas likely to impact Irish businesses as well as some tips when planning for 2021:
1. The implications of the Covid vaccine on Irish businesses. Cashflow and succession planning have become very important for business owners, however some good has come from Covid in terms of the opportunities it has created for doing business in a new way. It may also bring about potential M&A and real estate activity, and possible increased consumer spending in the year ahead.
2. Brexit and planning around UK businesses setting up operations in Ireland.
3. Budget 2021 Capital Acquisition and Gains taxes, Entrepreneurial Relief, Pensions and Retirement Relief.
We hope you enjoy listening to our podcast and if you have any questions regarding any of the points raised please let us know.
December 17, 2020
Taxation
Some Highlights of Budget 2020
Minister for Finance Paschal Donohoe delivered his Budget 2020 speech on Tuesday which included a €2.9bn budget day package. Also confirmed is a €1.2bn Brexit-proof fund.
Whether you are for or against it, carbon tax will be the most controversial element of the package and a talking point for many. Below we have outlined the main tax highlights of Budget 2020.
Personal Taxes
- Income tax rates and bands and the USC rates and bands remain unchanged. The Minister for Finance did not want to commit to personal tax cuts in the lead up to a no-deal Brexit.
- The Home carer credit has increased to €1,600 and the Earned income credit has increased to €1,500.
- The Group A threshold for CAT has increased from €320,000 to €335,000. The increased threshold applies to gifts or inheritances received on or after 9 October 2019.
- There was no mention of employer’s PRSI however Budget 2019 announced this would increase from 10.95% to 11.05% from 1 January 2020. Employer’s PRSI has steadily increased over the last few years and represents a significant cost to businesses.
- SARP relief and the Foreign Earnings Deduction have been extended to 31 December 2022.
- In 2018, the Government implemented a 0% BIK rate for electric vehicles subject to a value limit of €50,000 in comparison to a rate of 30% of the car’s original market value for non-electric vehicles. This initiative has been extended to 2022.
- An increase in the credit from 25% to 30%.
- The ability to claim the credit on qualifying expenditure before the company commences trading. It should be noted that any credit claimed in this period can only be offset against VAT and payroll liabilities.
- An increase in the outsourcing limit applicable to third level institutes from 5% to 15%.
- Farm restructuring relief, a capital gains tax relief due to expire at the end of this year, has been extended to 31 December 2022.
- Several amendments will be made to the KEEP scheme to incentivise take-up in the scheme. This includes a change in the definition of a qualifying company so that the scheme applies to group structures and a change in the definition of a qualifying individual so that it applies to part-time and flexible employees.
- EII relief, an income tax relief for individuals who invest funds in certain companies, will also undergo changes which apply from yesterday. The amendments will allow individuals to claim full relief in the year of investment and the annual investment limit will increase from €150,000 to €250,000.
- The Minister for Finance announced there will be a significant overhaul to the DWT regime. From 1 January 2021, real-time date collected under the new PAYE Modernisation regime will be used to create a personalised rate of DWT on distributions received by individuals. In the meantime, an increase in the DWT rate from 20% to 25% will apply from 1 January 2020.
October 9, 2019
Corporation Tax
SME’s Welcome Changes to Subsistence Allowance Rates
The Minister for Public Expenditure and Reform has amended the standard rates of subsistence allowance in Ireland that apply to the Civil Service. This greatly benefits the private sector, as the Civil Services rates provide the benchmark for Revenue approved flat rate allowances.
The benefits are twofold:
 What remains unchanged?
What remains unchanged?
 For more information please contact a member of our team or email us at info@robertsnathan.com
For more information please contact a member of our team or email us at info@robertsnathan.com
- Employees and directors can now claim back an additional 10% of the costs incurred completely Tax Free while travelling on business.
- The cost to companies is considered to be an allowable expense for Corporation tax purposes, meaning it can be deducted from taxable profits.
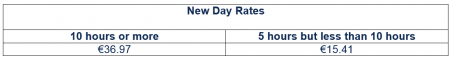
- The daily subsistence ‘5 Hour but less than 10 Hour’ rate increases by 10%.
- The daily subsistence ‘10 hours or more’ rate increases by 10%.
- The increases are in line with the Consumer Price Index.
- The revised standard rates of subsistence allowance are effective from 1 July 2019.
 What remains unchanged?
What remains unchanged?
- The standard overnight rate will not be increased.
- A separate Vouched Accommodation (VA) rate continues to apply whereby employees encounter difficulties in sourcing suitable accommodation in Dublin.
 For more information please contact a member of our team or email us at info@robertsnathan.com
For more information please contact a member of our team or email us at info@robertsnathan.com
August 9, 2019

